Menu
-
About Vitamin D:
- Vitamin D2
- Vitamin D3
- Sources of Vitamin D
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Vitamin D3 Receptors (VDR)
- Vitamin D Binding Proteins (DBP)
- Ideal Dosage of Vitamin D
- Contraindications for Vitamin D

What is Vitamin D?
- Since its discovery in 1920, Vitamin D is known to be an important nutrient, which plays a vital role in:
- regulating the body levels of calcium and phosphorus
- the mineralization of bone.
- Vitamin D may also play a role in supporting a healthy immune system.
-
Researchers are currently investigating the role Vitamin D could potentially play
in MS and also in lowering the risk of getting certain cancers. - Vitamin D carries out many of its functions in tandem with Vitamin K2.
-
Vitamin D stimulates the production of Vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDP's),
which (when activated by Vitamin K) shuttle calcium ions: - FROM where they should NOT be:
- heart valves
- arterial linings
- kidneys
- TO where they SHOULD be:
- bones
- teeth
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is synthesized by human skin through the process of photosynthesis.
- photochemical cleavage of cutaneous 7-dehydrocholesterol
- most efficient at ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths
- The ability to convert 7-dehydrocholesterol into vitamin D in the skin decreases with age.
- Structually, Vitamin D consists of a group of fat-soluble molecules called secosteroids
- pre-hormones
- similar to steroids (but with "broken" rings)
- Vitamin D3 is a biologically inactive pre-hormone
- to become active, Vitamin D must undergo two successive hydroxylations:
-
first in the liver (on carbon 25) to form 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]
(a pro-hormone named calcifediol aka calcidiol) -
then in the kidneys (on carbon 1) to form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)(2)D],
which is the biologically active form of vitamin D (a hormone named calcitriol) - Calcitriol, is a potent steroid hormone and has biologic effects which extend far beyond control of mineral metabolism.
- There are many receptors for calcitriol, aka "Vitamin D receptors" (VDR) present in a wide variety of cells through out the body.
- As the concentration of calcitriol increases . . .
- (VDR) throughout the body become stimulated
- causing activation of gene transcription
- Interaction between calcitriol and VDR sites in various organs produce numerous biological actions:
- regulation of calcium and phosphorus in the intestines and bones
- insulin sensitivity and secretion
- regulation of cellular growth and angiogenesis
- renin expression and inhibition of vascular smooth muscle proliferation
- inflammation and amyloid plaque formation in the brain
- Contrary to common belief, Vitamin D is NOT actually a vitamin.
-
"Vitamins" by definition, are nutrients that CANNOT be produced by the body,
but are NECESSARY for the proper functioning of the body's tissues and organs. - Vitamin D was originally classified as a vitamin because of the findings of a British researcher in 1920, who raised dogs in the winter (without any exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet rays).
- He found that the animals developed rickets (a bone disease) unless fed a diet containing fish-liver oils.
- He wrongly concluded that the fat soluble substance needed for developing bones was not found naturally in the body and so was a "vitamin".
- In 1924 researchers discovered that exposing skin to sunlight resulted in the body's own production of this so-called "fat-soluble vitamin".
- Despite the misnomer, for nutritional and public health reasons, vitamin D continues to be officially classified as a "vitamin".
There are two basic types of Vitamin D . . . or are there?
- A vitamer is defined as a member of a family of chemical related compounds, each with similar molecular structures and each with the ability to function as a unique vitamin.
- Vitamin D is often said to consist of two vitamers (Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3).
- This characterization is a misnomer
- We've already discussed that Vitamin D is not really a true Vitamin
- Although humans can NOT synthesize Vitamin D2, we can synthesize Vitamin D3
- Vitamin D2 is best described as a Vitamin D analog.
- For the sake of conforming with convention, lets just "say" that Vitamin D exists in two forms:
- ergocalciferol
- plant form
- Fortified food, supplementation
- can NOT be synthesized by the body
- Doctor RX required
-
HALF as effective at improving
Vitamin D Status -
Longer half life, far MORE prone to
toxicity issues with large dose -
Metabolized by the liver into
25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (calcidiol) -
Metabolized by the kidneys into
1.25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (calcitriol) - cholecalciferol
- animal form
- fish oils, egg yolk, butter, liver and supplementation
- synthesized when skin is exposed to sunlight
- No RX needed
-
TWICE as effective at improving
Vitamin D Status -
Shorter half life, far LESS prone to
toxicity issues with large dose -
Metabolized by the liver into
25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcidiol) -
Metabolized by the kidneys into
1.25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) - In plants, when ultraviolet light from the sun, hits the leaves . . .
- ergosterol (in the plant cells) is converted to Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
- In humans, when ultraviolet light from the sun, hits the skin . . .
-
cholesterol aka Pro-Vitamin D, (a squalene metabolite in skin cells),
is converted to Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). - Neither Vitamin D2 nor D3 have significant biological activity until:
- first metabolized by the liver into calcidiol (the pro-homone form of Vitamin D)
- then converted by the kidneys into calcitriol (the fully-active, hormonal form of Vitamin D)
- Ergocalciferol (which is NOT really Vitamin D) is more aptly described as a Vitamin D analog.
- Ergocalciferol was a patented drug before the patent ran out.
-
Ergocalciferol is produced by irradiation of ergosterol,
a membrane sterol found in the ergot fungus. -
Ergocalciferol is the commonly prescribed "Vitamin D" by M.D.'s
and has been associated with most of the Vitamin D toxicity cases - Ergocalciferol should be avoided.
Vitamin D2
Vitamin D3
Sources of Vitamin D
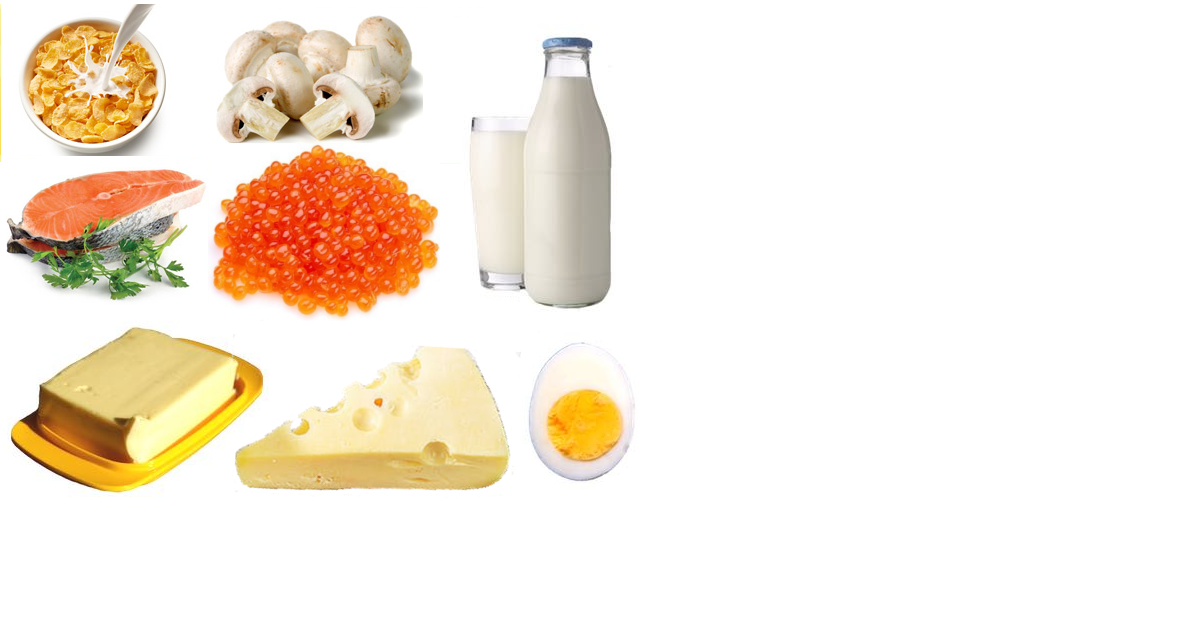

- Humans take in Vitamin D through:
- Natural foods
- salt water fish such as herring, salmon, sardines, and fish liver oils
- The average person's diet is very low in Vitamin D.
- Fortified foods
- Since the 1930's foods such as milk, margarine, butter, cereals and chocolate mixes have been fortified with Vitamin D (typically a mix of both D2 and D3).
- Prior to the 1930s, rickets was a major public health problem in the United States.
- Rickets is now very uncommon.
- Milk in the United States is fortified with 10 micrograms (400 IU) of vitamin D per quart.
- Human milk does not typically contain adequate Vitamin D.
- Vitamin D supplements are often recommended for exclusively breast-fed infants.
- Sunlight exposure
- Exposure to sunlight is an important source of Vitamin D.
- Ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight trigger vitamin D synthesis in the skin.
- Many populations through out the world are exposed to quite suboptimal levels of sunlight, especially during the winter months (resulting in lower Vitamin D status).
- Other factors that reduce exposure to UV rays from sun and lower Vitamin D status:
- spending a lot of time indoors
- living in cities that have tall buildings
- wearing clothes that cover most of the body
- using synthetic sunscreens
- air pollution
- Under these conditions vitamin D is a true vitamin, because it must be consumed (either through food or supplementation) to maintain optimal health.
- Supplementation
- Vitamin D2
- Should be avoided
- can only be prescribed by a doctor
- Vitamin D3
- preferred over D2
- no prescription needed
- lanolin-derived (from wool-bearing animals like sheep)
- purified and crystallized
- chemically processes to produce 7-dehydrocholesterol.
- liquified and then exposed to ultraviolet radiation to produce Vitamin D3
- fish oil-sourced
- Fish liver oils and the flesh of high-fat fish such as tuna and salmon are among the few foods that naturally contain significant amounts of vitamin D.
- Cod liver oil contains a higher amount of vitamin D than other food sources such as eggs, beef liver and milk.
- What's a better source of Vitamin D3?
- According to John Jacob Cannell, MD, (Executive Director of the Vitamin D Council)
- There is no difference between Vitamin D3 derived from lanolin or fish oil
Vitamin D Deficiency

- Research from the last two decades suggest vitamin D may be a factor in supporting health beyond just the prevention of rickets in children.
- In addition to causing rickets, inadequate vitamin D also prevents children from attaining their genetically programmed peak bone mass
- could be a contributing factor to:
- osteoporosis in adults
- osteomalacia - an often painful bone disease
- Adequate vitamin D is also important for proper muscle functioning.
-
Researchers are investigating the impact Vitamin D deficiency could have on
- MS
- diabetes
- hypertension
- common cancers
- Vitamin D inadequacy has been reported in approximately 36% of otherwise healthy young adults and up to 57% of general medicine inpatients in the United States and in even higher percentages in Europe.
- Recent epidemiological data document the high prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy among elderly patients and especially among patients with osteoporosis.
-
contributing factors to the high prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy include:
- low sunlight exposure
- age-related decreases in cutaneous synthesis
- diets low in vitamin D
-
Supplemental doses of vitamin D and sensible sun exposure could prevent
Vitamin D deficiency/inadequacy in most of the general population.
- The classical function of Vitamin D, in which calcitriol (the active form of Vitamin D) stimulates "Vitamin D receptors" (VDR) in the intestines to facilitate mineral balance and skeletal maintenance, has been known for many years.
- With the discovery of vitamin D receptors in other various tissues though out the body . . .
- there has been increased recognition of some non-classical biological functions of vitamin D, such as regulation of cellular proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and innate and adaptive immunity.
- Researchers are now investigating the role these non classical functions may play in cancer, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular, and autoimmune and dermatological diseases.
- VDRs belong to the nuclear hormone receptor family of superfamily (NR1I1)
- VDRs function as a ligand-inducible transcription factor.
-
Most of the biological actions of vitamin D are now thought to
take place through the VDR-mediated control of target genes. - As the concentration of calcitriol increases . . .
- (VDR) throughout the body become stimulated
- causing activation of gene transcription
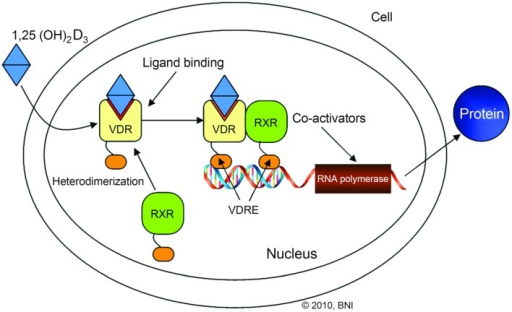
- Calcitriol binds to the VDR
- forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor.
- Then binds to hormone response elements on DNA resulting in expression or transrepression of specific gene products, which influence the production of RNA which encodes proteins that are integral to specific biological activities.
-
The genes and gene networks that have been identified as responsible
for these biological actions of calcitriol are extensive: - Calcitriol plays a central role in regulating mineral metabolism via its actions in intestinal and kidney epithelial cells and in specific bone cells.
- Surprisingly, while many target genes, which play important roles in calcium and phosphorus homeostatic have been identified, additional targets important to these processes continue to be discovered.
- calcium and phosphate transporters and their associated basolaterally-located, energy-driven ion pumps in the intestine and kidney
- osteoblast-synthesized osteoclastogenic differentiation factor receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)
- stimulates the activity of existing bone-resorbing osteoclasts
- prolongs their lifespan
- induces the formation of new replacements
- bile acid metabolism in the colon
- degradation of xenobiotic compounds in several tissues
- differentiation of keratinocytes in skin
- development and cycling of dermal hair follicles
- key cell types involved in both innate and adaptive immunity
- VDR themselves are encoded by the VDR gene.
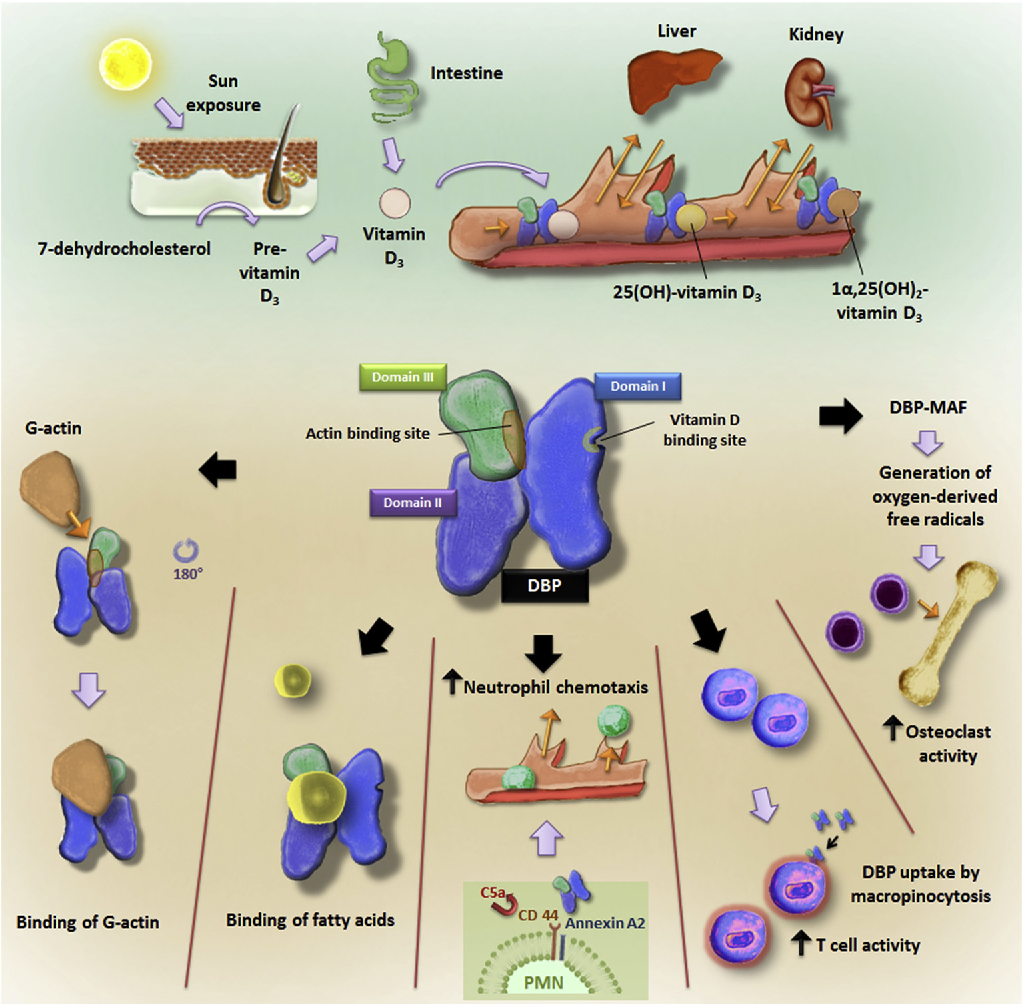
- All the various forms of Vitamin D (Vitamin D2, Vitamin D3, calcidiol and calcitriol) require special proteins (Vitamin D Binding Proteins aka VBD) that have the ability to bind to and transport vitamin D (and its metabolites) between skin, liver and kidney, and then on to the various target tissues.
- DBP aka gc-globulin (group-specific component), is a protein that is encoded (in humans) by the GC gene.
- DBP belong to the albumin gene family, together with human serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein. It is a multifunctional protein found in plasma, ascitic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid and on the surface of many cell types.
- The major proportion of vitamin D in blood is bound to DBP.
- While it is best known for its vitamin D binding properties, DBP may have roles in other biological processes as well.
Vitamin D Status
- Regardless of if Vitamin D3 (a pre-homone called cholecalciferol) is produced in the skin or ingested in the diet, it is biologically inert, requiring two successive hydroxylations to become biologically active:
-
first in the liver on (carbon 25) to form 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D]
(a pro-hormone named calcifediol aka calcidiol) -
then in the kidneys (on carbon 1) to form 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)(2)D],
which is the biologically active form of vitamin D (a hormone named calcitriol) -
With the identification of 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)(2)D, methods were developed to
measure these metabolites in the circulation. -
1,25(OH)D3 is the biologically active form of vitamin D,
however its measurement is NOT an ideal indicator for vitamin D status - 25(OH)D turns out to be a MUCH better barometer for vitamin D status.
-
The only way to determine if a person is vitamin D deficient or sufficient
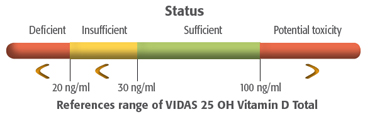
is to measure their circulating level of 25(OH)D. - Most experts agree that:
- a level of <20 ng/mL is considered to be vitamin D deficiency
- a level of 21-29 ng/mL is considered to be insufficient.
-
A level >30 ng/ml is considered to be a healthful level for all
children and adults to maintain throughout the year.
Vitamin D Dosage
-
Vitamin D3 amounts are most often referred to in iu (international units)
though sometimes referred to in mg. - 1 mg of vitamin D3 is equal to 40,000 iu (1 mcg of D3 is equal to 40 iu).
-
The IOM (Institute of Medicine) of the National Academy has NOT established an RDA
(Recommended Dietary Allowances) for Vitamin D. -
The IOM has established an AI (Adequate Intake) for Vitamin D of 200 iu/day for otherwise
healthy persons to avoid metabolic bone disease. -
Recent research suggests 5,000 iu/day of cholecalciferol is optimum for those, who do not have
regular year-round sun exposure. - Other researchers, including Robert Barefoot have suggested Vitamin D3 doses as high as 30,000 iu/day.
- Most brands on the market contain 200 to 400 iu of Vitamin D per capsule.
- D-Max contains 5,000 iu (equal to .125 mg or 125 mcg) of Vitamin D3 per capsule.
- Vitamin D Toxicity Fear is Unwarranted
- According to John Jacob Cannell, MD, (Executive Director of the Vitamin D Council):
- In 1999, Professors Reinhold Vieth indirectly asked the medical community to produce any evidence 10,000 units of vitamin D a day was toxic, saying:
- Even Ian Monroe, the chair of the relevant IOM committee, wrote to the Journal to compliment Vieth's work and to promise his findings will be considered at the time of a future Institute of Medicine review.
- Cholecalciferol Is Safe, Ergocalciferol is not
- Like most medication, cholecalciferol is certainly toxic in excess, and, like Coumadin, is used as a rodent poison for this purpose.
- Animal data indicates signs of toxicity can occur with ingestion of 0.5 mg/kg (20,000 IU/kg).
- The oral LD50 (the dose it takes to kill half the animals) for cholecalciferol in dogs is about 88 mg/kg, or 3,520,000 IU/kg.
- This would be equivalent to a 110 pound adult taking 176,000,000 IU or 440,000 of the 400 unit cholecalciferol capsules.
- Vieth reports human toxicity probably begins to occur after chronic daily consumption of approximately 40,000 IU/day (100 of the 400 IU capsules).
"Fear of vitamin D toxicity is unwarranted, and such unwarranted fear, bordering on hysteria, is rampant in the medical profession."
"Throughout my preparation of this review, I was amazed at the lack of evidence supporting statements about the toxicity of moderate doses of vitamin D." He added: "If there is published evidence of toxicity in adults from an intake of 250 ug (10,000 IU) per day, and that is verified by the 25(OH)D concentration, I have yet to find it."
"Although there are documented cases of pharmacological overdoses from ergocalciferol, the only documented case of pharmacological, not industrial, toxicity from cholecalciferol we could find in the literature was intoxication from over the counter supplement called Prolongevity. On closer inspection, it seemed more like an industrial accident but is interesting because it gives us some idea of the safety of cholecalciferol. The capsules consumed contained up to 430 times the amount of cholecalciferol contained on the label (2,000 IU). The man had been taking between 156,000B2,604,000 IU of cholecalciferol a day (equivalent to between 390B6,500 of the 400 unit capsules) for two years. He recovered uneventfully after the proper diagnosis, treatment with steroids and sunscreen."
"It is true that a few people may have problems with high calcium due to undiagnosed vitamin D hypersensitivity syndromes such as primary hyperparathyroidism, granulomatous disease or occult cancers but a blood calcium level, PTH, 25(OH)D, and calcitriol level should help clarify the cause of the hypersensitivity. Although D can be toxic in excess, the same can be said for water."
Vitamin D Contraindications
Vitamin D should NOT be taken by anyone who has primary hyperparathyroidism, sarcoidosis, granulomatous disease, or other conditions that cause high blood calcium.
Vitamin D3 and Bone Health

- Since its discovery in 1920, Vitamin D has been linked to bone health.
- Vitamin D helps support normal blood levels of calcium and phosphorus.
- aids in the absorption of calcium
- targets Vitamin D receptor sites in the small intestine
- dramatically increases the uptake of calcium.
- regulates the remodeling of bone
- interacts with the parathyroid glands
- controls bone resorption and serum calcium levels.
- increases reabsorption of phosphate by the renal tubules
-
stimulates the production of Vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDP's),
which (when activated by Vitamin K) shuttle calcium ions: - FROM where they should NOT be:
- heart valves
- arterial linings
- kidneys
- TO where they SHOULD be:
- bones
- teeth
- Without adequate vitamin D, bones can become thin, brittle, soft, or misshapen . . .
- characteristic of the following bone diseases:
- Rickets
- a bone disease related to the failure of the osteoid to calcify
- affects children who are vitamin D deficient.
- causes progressive softening and weakening of the bones' structure.
- results in bones becoming flexible and gradually molded by forces such as bearing weigh exerted on them.
- Children with rickets may not grow to their full potential and may develop deformities of the body structure such as knonk-knees or bowed legs.
- At the early part of the 20th century, rickets remained one of the most devastating health consequences of the Industrial Revolution.
- It been estimated that more than 90 percent of children in Northern Europe and 80 percent of children in Boston and New York City showed evidence of this bone deforming disease.
- As early as 1822 Sniadecki identified the importance of sun exposure for preventing growth retardation and skeletal deformities associated with rickets noting that children living in the inner city of Warsaw had a high incidence of rickets whereas children living in adjacent rural areas did not.
- This was followed by the insightful observations in 1889 by Palm that children living in London and Glasgow were plagued with rickets, while children who lived in Asia and India were free of the disease. He recommended that children from the inner cities be exposed to sunlight and encouraged sunbathing as a preventive and treatment strategy.
- At that time however, the medical community, found it inconceivable that skin exposure to sunlight could have any beneficial effect for bone health.
- In the 1930s, public health initiatives in the USA, recommended fortifying every cup of commercially sold milk with 100 iu's of vitamin D.This fortification program is still in effect today, and the incidence of rickets in the USA is very low.
- Osteomalacia
- Osteomalacia is basically the same disease as rickets but occurring in adults.
- Seniors in northern climates and adults, who do not receive direct sunlight for at least 45 minutes per week are most susceptible.
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by fragile bones, resulting in an increased risk of bone fractures. It is estimated that over 25 million adults in the United States have, or are at risk of developing osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is most common in post menopausal women.
- Adequate calcium and vitamin D throughout life, along with physical activity, may reduce the risk of osteoporosis in later life.
- Osteoarthritis
- Arthritis and its associated symptoms occur because of the breakdown of cartilage in the joints.
- Just as vitamin D may help support healthy bones, it may also help support the maintenance of healthy cartilage.
- There are many ongoing research studies, looking into the relationship between low intakes of vitamin D and the risk of getting arthritis. The research is very promising.
Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Health

- Atherosclerosis
- 2018
Vitamin D status in coronary artery disease: association with IL-35 and TGF-β and disease severity
Rasa F, Naderi N, Eftekhar E, Mansoori E, Rahimzadeh M. ndocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2018 Apr 25. doi: 10.2174/1871530318666180426101756 - 81 patients were divided into single (n= 20), double (n=20) and triple (n=20) vessel disease groups and compared to no vessel disease (No VD) group (n=21). Interleukin (IL) -35 and TGF-β were measured using ELISA. Vitamin D was measured using Electrochemiluminescence assay.
- The results suggested that, although decreased TGF-β and IL-35 plasma levels correlate positively with decreased vitamin D levels and negatively with severity of CAD, only TGF-β has a significant association with vitamin D deficiency in CAD patients. It seems that the arterial support of vitamin D is at least partly attributed to the up-regulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines especially TGF-β.
- High Blood Pressure
-
2018
Associations of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D With the Blood Pressure Response to Maximal Exercise Among Healthy Adults
Zaleski A, Taylor B, Armstrong B, Puglisi M, Clarkson P, Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2018 Aug 30:1-21. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2017-0424. - Insufficient 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are associated with high resting blood pressure (BP).
- In this study, the relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the peak systolic BP (SBP) response to exercise, (a predictor of future hypertension) was investigated.
Vitamin D and Dental Health
- 2018
Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis
Anbarcioglu E, Kirtiloglu T, Ozturk A, Kolbakir F, Ackgoz G, Colak R. Oral Dis. 2018 Aug 31. doi: 10.1111/odi.12968 - Vitamin D deficiency is linked to several infectious and inflammatory conditions, including periodontal disease.
- This study evaluated the association between vitamin D concentration and periodontal disease, both Aggressive (AgP) and chronic (CP) periodontitis.
- Researchers suggest that given the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in AgP patients, vitamin D deficiency may be a potential risk factor for AgP.
- 2004 Association between serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and periodontal disease in the US population
Dietrich T, Joshipura KJ, Dawson-Hughes B, Bischoff-Ferrari HA., Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Jul;80(1):108-13. - This study evaluated whether serum 25-hydroxyvitamin+D3 concentrations are associated with Periodontal disease (PD) in the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- The researchers analyzed data on periodontal attachment loss (AL) and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin+D3 concentrations from 11 202 subjects aged > or =20 y were . Mean AL was modeled in a multiple linear regression with quintile of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin+D3 concentration as an independent variable. The model was stratified by age and sex and was adjusted for age within age groups, race or ethnicity, smoking, diabetes, poverty income ratio, body mass index, estrogen use, and gingival bleeding.
- The researchers concluded that low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin+D3 concentrations may be associated with PD independently of BMD. Given the high prevalence of PD and vitamin D deficiency, these findings may have important public health implications.
Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis
- Michael Holick, MD, PhD is the director of the Vitamin D Research Lab at Boston University Medical Center, and is considered by many to be the nation's leading authority on vitamin D.
-
according to Hollick:
"It's been well-known that if you live at a higher latitude, where there's less sun exposure, you're at a higher risk of developing MS", Conversely, if you live in a sunny climate where vitamin D Vitamins can be easily absorbed year-round from sunlight for your first 10 years, it imprints on you a decreased MS risk that can last a lifetime"
- 2018 Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review
Martina B. Sintzel, Mark Rametta, Anthony T. Reder; Journal ListNeurol Therv.7(1); 2018 JunPMC5990512 - a comprehensive exploration of the the hypothesis that there is a correlation between the level of serum vitamin D and MS risk and disease activity
- large, prospective, observation studies, epidemiological studies, and studies using new approaches such as Mendelian randomization was conducted.
- ongoing research included in this review suggest that the level of serum calcidiol level affects the risk of developing MS and also modifies disease activity in MS patients.
- 2018 High-dose ω-3 Fatty Acid Plus Vitamin D3 Supplementation Affects Clinical Symptoms and Metabolic Status of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.
Kouchaki E1, Afarini M, Abolhassani J, Mirhosseini N, Bahmani F, Masoud SA, Asemi Z., J Nutr. 2018 Aug 1;148(8):1380-1386. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxy116. - This study aimed to determine the effects of ω-3 fatty acid and vitamin D cosupplementation on the disability score and metabolic status of patients with MS.
- This was a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score and inflammation as primary outcomes and oxidative stress biomarkers and metabolic profile as secondary outcomes.
- Patients, aged 18-55 y, were matched for disease EDSS scores, gender, medications, BMI, and age (n = 53) and randomly received a combined 2 x 1000 mg/d ω-3 fatty acid and 50,000 IU/biweekly cholecalciferol supplement or placebo for 12 wk.
- Fasting blood samples were collected at baseline and end of intervention to measure different outcomes. Multiple linear regression models were used to assess treatment effects on outcomes adjusting for confounding variables.
- Dr. Kassandra Munger Sc.D from the Harvard School of Public Health has been researching the role Vitamin D plays in MS, since 2004.
- 2004 Vitamin D intake and incidence of multiple sclerosis
Munger KL, Zhang SM, O'Reilly E, Hernan MA, Olek MJ, Willett WC, Ascherio A., Neurology. 2004 Jan 13;62(1):60-5. - Landmark study reviewed 20 years of data from Nurses' Health Study
Vitamin D3 and Diabetes
The relationship between Vitamin D deficiency and diabetes is a widely researched subject. Studies through out the world have been conducted on animal, infant and adult subjects.
- 2018
A double blind randomized clinical trial to investigate the effect of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic and hepato-renal markers in type 2 diabetes and obesity
Safarpour P, Vafa MR, Amiri F, Janani L et al. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2018 Apr 28;32:34. doi: 10.14196/mjiri.32.34. eCollection 2018. - According to the recent studies, vitamin D deficiency has been correlated with progress in type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome.
- This clinical trial study assessed the effect of vitamin D supplementation on glucose and lipid profiles, blood pressure, and biomarkers of liver and kidney in type 2 diabetic patients
- 90 patients with type 2 diabetes and serum 25-Hydroxy vitamin D levels of less than 30 ng/ml were recruited from "Besat Diabetes Clinic" in Rasht, North of Iran. The subjects took 50000 IU vitamin D supplements or placebo for 8 weeks. The researchers assessed the levels of serum 25 (OH) vitamin D, glucose and lipid profiles, oxidative and inflammatory indices, liver and kidney biomarkers, blood pressure, and sun exposure time, physical activity before and after intervention, and compared them between cases and controls
A number of studies have taken place in northern Finland, which has the highest reported incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world and interestingly only receives two hours of sunlight during December.
In one such study, researchers followed more than 10,000 pregnant women living in northern Finland, who were due to give birth in 1966. New mothers recorded whether they gave vitamin D supplements to their children and how much they provided, during the first year of life. Researchers tracked the number of children who developed type 1 diabetes over 40 years.
Another norwegian study was conducted to find out whether the intake of vitamin D taken by either mothers during pregnancy or by children during the first year of their life, was linked to lowering the risk of type 1 diabetes among children.
The nationwide case-control study was done in Norway and consisted of 545 children diagnosed with type 1 diabetes and 1,668 control participants. Families were sent a questionnaire in the mail and were required to answer questions pertaining to the number of times they used cod liver oil or other vitamin D supplements.
Researchers were very impressed with the study results.
Read LessVitamin D and Cancer
It is believed that vitamin D and its metabolites, play an important part in the regulation of genes involved in cell growth, differentiation and proliferation.
These important properties have prompted researchers to investigate if there is a link between vitamin D deficiency and cancer.
Laboratory, animal, and epidemiologic studies have looked at the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and cancer. Clinical studies have focused on the four most common cancers:
- Breast
- Prostate
- Colon
- Skin
The results of these studies have been quite compelling and many researchers in this field are very excited about future studies.
For more than 50 years, documentation in the medical literature suggests regular sun exposure is associated with substantial decreases in death rates from certain cancers and a decrease in overall cancer death rates. Recent research suggests this is a causal relationship that acts through the body's vitamin D metabolic pathways. For instance, some evidence points to a prostate, breast and colon cancer belt in the United States, which lies in northern latitudes under more cloud cover than other regions during the year. Rates for these cancers are two to three times higher than in sunnier areas.
Dark-skinned people require more sun exposure to make vitamin D. The thickness of the skin layer called the stratum corneum affects the absorption of UV radiation. Black human skin is thicker than white skin and thus transmits only about 40 percent of the UV rays for vitamin D production. Darkly pigmented individuals who live in sunny equatorial climates experience a higher mortality rate (not incidence) from breast and prostate cancer when they move to geographic areas that are deprived of sunlight exposure in winter months. The rate of increase varies, and researchers hesitate to quote figures because many migrant black populations also have poor nutrition and deficient health care that confound statistics somewhat.
Although excessive sun exposure may give rise to skin cancer, researchers as early as 1936 were aware that skin cancer patients have reduced rates of other cancers.
Read LessVitamin D3 and Obesity
Have you ever wondered why some people can eat all they want and not get fat, while others are constantly battling extra pounds? Could the answer have to do with vitamin D and calcium status?
This question is the subject of vast research. Researchers are looking for a link between Vitamin D deficiency and obesity.
- 2018 Vitamin D supplementation and body fat mass: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Golzarand M, Hollis BW, Mirmiran P, Wagner CL, Shab-Bidar S., Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018 Mar 21. doi: 10.1038/s41430-018-0132-z. - The objectives of this study was to investigate the association between vitamin D3 and PFM pooling together observational studies and RCTs
- PubMed/MEDLINE, Cochrane, and Scopus were comprehensively searched from inception to September 2016. The Fisher's Z (SE) of correlation coefficient and mean (SD) of changes in PFM from baseline were used to perform meta-analysis in observational studies and RCTs, respectively. To determine potential source of heterogeneity, subgroup and meta-regression analyses were conducted
- The researchers concluded that 25(OH)D level is inversely correlated with PFM but cholecalciferol supplementation had no effect on PFM.
- 2018 Effect of vitamin D supplementation on anthropometric indices among overweight and obese women: A double blind randomized controlled clinical trial
Roosta S, Kharadmand M, Teymoori F, Birjandi M, Adine A, Falahi E., Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018 Jul;12(4):537-541. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.03.022. Epub 2018 Mar 27. - The aim of this study was to investigate effect of vitamin D supplementation on anthropometric indices among women with overweight and obesity.
- This double blind randomize clinical trial was conducted on 66 overweight and obese women. Those in intervention group received oral supplement of vitamin D 50,000 IU (1250 mcg) per 25 day and in control group participants received placebo for 3 months. Anthropometric indices were measured before and after 3 months intervention. Before the intervention a 24-h dietary recall (3 days) were used to assess dietary intake of individuals. Independent test and multivariate repeated measure were used to data analysis.
- The researchers concluded that supplementation with vitamin D 50,000 iu/day for 3 months resulted in a significant reduction in anthropometric indices in women with obesity and overweight with normal primary 25(OH) D3 serum levels.
D Max®
Contains:
- 5,000 iu's of Vitamin D3 per capsule
- 250 capsules per bottle
Suggested use:
1 capsule twice per day
Dmax is a great value . . .
While many Vitamin D3 products come in a 60 count bottle, each bottle of Dmax contains 250 capsules. Based on the single bottle price ($22.95), the cost of D Max is less than $2.75 per month. (even less when buying larger quantities)

- 1 bottle
- $23.95
- 2 bottles $22.95 each
- $45.90
- 3 bottles $21.95 each
- $65.85
- 6 bottles $19.95 each
- $119.70
- 12 bottles $17.95 each
- $215.40
- 24 bottles $15.95 each
- $382.80
D Max: Supplement Facts
| Serving Size: 1 Capsule
Capsules per container: 250 Servings per container: 250 |
||
| Amount per Serving | % Daily Value | |
|---|---|---|
|
Vitamin D3 (non GMO cholecalciferol) (from sheep lanolin) (100,000 iu/gm) |
125 mcg (5,000 IU) | 625% |
Other ingredients: Microcrystalline Cellulose, Gelatin, L-Leucine
Directions:
Take 1 capsule, once per day (or as directed by your health care provider).
vK2®
Contains:
60 capsules per bottle
(30 day supply)
- MK-4 (5 mg/capsule)
- MK-7 (100 mcg/capsule)
Suggested use:
1 capsule twice per day
(or one capsule for each Dmax capsule taken)

vK2® is the perfect compliment to Dmax
- 1 bottle
- $30.95
- 2 bottles $29.95 each
- $59.90
- 3 bottles $28.95 each
- $86.85
- 6 bottles $27.95 each
- $167.70
- 12 bottles $25.95 each
- $311.40
- 24 bottles $23.95 each
- $574.80
vK2® Supplement Facts
| Serving Size: 1 Capsule
Capsules per container: 60 Servings per container: 60 |
||
| Amount per Serving | % Daily Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin K2 (pharmaceutical grade) | 5.1 mg | 6154% |
|
Menaquinone-4 (100% TRANS form MK-4) |
5.0 mg | * |
|
Menaquinone-7 (70% TRANS form MK-7) |
.1 mg (100 mcg) | * |
*Daily value not established.
Other ingredients: Vegetable capsule, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Rice Flour
Directions:
Take 1 capsule 1 time per day,
or
Take 1 capsule for each 5,000 iu of Vitamin D3 you take
or
Take as directed by your health care provider
D Max-vK2 Combo®
Suggested use:
one capsule of vK2® for each capsule of D Max taken

- (1) bottle D Max
+ (4) bottles vK2 - $124.95
- (2) bottles D Max
+ (8) bottles vK2 - $245.95
Coral Calcium “Marine Plus”
Coral Calcium: "Marine Plus" is based on the original Coral Calcium Supreme formula that Bob Barefoot used to sell on TV. We've upgraded his 1,000 mg serving size to 1,500 mg. Each 3 capsule serving of "Marine Plus" contains 1,500 mg of "marine grade" coral calcium from Okinawa, Japan, which has the biologically perfect 2 to 1 ratio of calcium to magnesium + 73 naturally occurring trace minerals + Aquamin + Vitamins (A, B, C, D3 & E) + Cesium.
Suggested use:
3 capsules per day
(preferably at regular intervals) with meals.

- 1 bottle - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" - $19.95
- 2 bottles - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" $17.95 each - $35.90
- 3 bottles - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" $16.95 each - $50.85
- 6 bottles - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" $15.95 each - $95.70
- 12 bottles - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" $14.95 each - $179.40
- 24 bottles - Coral Calcium:
"Marine Plus" $13.95 each - $334.80
Coral Calcium “Marine Plus”: Supplement Facts
| Serving Size: 3 Capsules
Capsules per container: 90 Servings per container: 30 |
||
| Amount per Serving | % Daily Value | |
|---|---|---|
|
Coral Calcium (SMP 44®) |
1,500 mg | * |
| Calcium | 375 mg | 37.5% |
| Magnesium | 187.5 mg | 46.5% |
| Strontium | 2.8 mg | * |
|
Marine Algae (AquaminF®) |
362.5 mg | * |
| Calcium | 116 mg | 12.2% |
| Magnesium | 58 mg | 15% |
|
Vitamin D3 (as Cholecalciferol) |
20.4 mcg (816 IU) | 102% |
|
Vitamin A (as Beta Carotene) |
2917 iu | 58% |
|
Vitamin B-1 (as thiamine HCL) |
1.1 mg | 73% |
|
Vitamin B-2 (as Riboflavin Pwd) |
1.2 mg | 71% |
|
Vitamin B-3 (as Niacinamide) |
14 mg | 70% |
|
Vitamin B-5 (as di-Calcium Pantothenate) |
7 mg | 70% |
|
Vitamin B-6 (as Pyndoxine) |
1.4 mg | 70% |
|
Vitamin B-12 (as Cyanocobalamin) |
4.3 mcg | 72% |
|
Vitamin C (as Ascorbic acid) |
70 mg | 117% |
|
Vitamin E (as d-alpha-tocopherol) |
35 iu | 117% |
| Folic Acid | 400 mg | 100% |
|
Zinc (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
16.4 mg | 109% |
|
Selenium (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
30 mcg | 43% |
|
Copper (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
2.4 mg | 120% |
|
Manganese (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
1.44 mg | 72% |
|
Chromium (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
86 mcg | 72% |
|
Boron (as Amino Acid Chelate) |
64 mcg | * |
|
Iodine (from Kelp) |
150 mcg | 100% |
|
Cesium (as chloride) |
3 mg | * |
*Daily value not established.
Other ingredients: Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, magnesium stearate
Directions:
Take 3 capsules per day (preferably at regular intervals) with meals.
Other Products available from: NHS Global Distributors LLC

Prostate Miracle®Advanced Formula
2nd generation upgrade to our original Prostate Miracle®. This highly effective, natural, time-tested formula contains pine derived beta sitosterol (NON GMO and NOT Chinese).
read more
LipoProstate Miracle™
3rd generation upgrade to - Prostate Miracle®, using our Advanced Liposomal Delivery System™ to overcome the absorption barriers that men with prostate and gut issues face.
read more
Sea of Greens®
A Whole-Superfood supplement, combining an optimal blend of sea vegetables and Freshwater algae.
read more
Pectin Plus®
Supports healthy detoxification, healthy blood pressure, healthy cholesterol levels and prostate health
read more
Estrogen Balance®
A natural formula for Men & Women, combining: D.I.M., Quercetin and Flaxseed.
read moreNavitagion Links
Contact
255 Rivertown Shops Dr.
Suite 102, PMB 128
Saint Johns, FL 32259
International: 1.805.322.0005
Thank you for visiting Vitamin-D-Max.com
This information here within is designed to provide accurate information in regard to the subject matter covered. It is provided with the understanding that NHS Global Distributors LLC. is not engaged in rendering medical advice. If expert assistance is required, the services of a competent medical professional should be sought. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Always read and follow manufacturer's directions that come with this product.
You are protected by the FDA Dietary Supplement and Nonprescription Drug Consumer Protection Act
please call 877.965.2140 or Click here to report any Adverse Reaction with Dmax.